Asal usul danau toba bahasa inggris – Danau Toba, sebuah permata tersembunyi di Sumatera Utara, menyimpan misteri yang memikat. Di balik keindahannya yang menawan, terbentang kisah geologis yang dramatis. Danau ini merupakan hasil dari letusan supervolcano dahsyat yang terjadi ribuan tahun silam. Letusan ini begitu kuat sehingga membentuk kaldera raksasa yang kini menjadi danau terbesar di Indonesia.
Kisah Danau Toba tak hanya menarik dari segi geologi, tetapi juga memiliki makna budaya yang dalam. Suku Batak, penduduk asli daerah ini, memiliki mitos dan legenda yang unik tentang asal usul danau ini. Mereka percaya bahwa Danau Toba tercipta dari sebuah tragedi, dan legenda ini menjadi bagian penting dari identitas budaya mereka.
The Geological Formation of Lake Toba
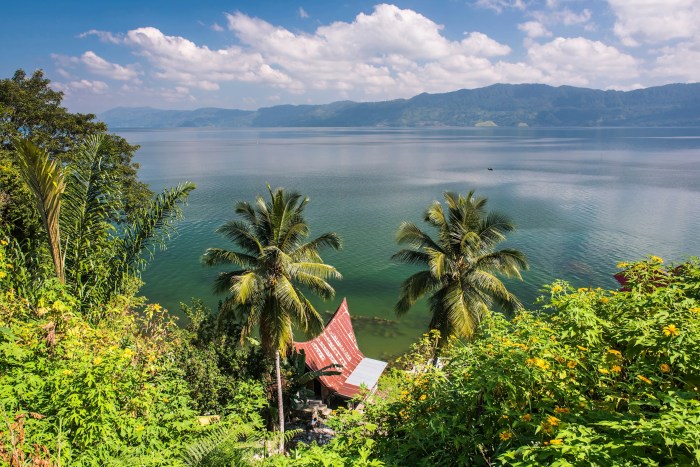

Lake Toba, nestled in the heart of North Sumatra, Indonesia, is a breathtaking spectacle of nature. This vast, sapphire-blue lake, the largest volcanic lake in the world, is a testament to the immense power of Earth’s geological forces. Its formation is a story of cataclysmic volcanic eruptions and the subsequent reshaping of the landscape.
The Volcanic Eruption that Shaped Lake Toba
The story of Lake Toba begins with a colossal volcanic eruption, one of the most powerful in Earth’s history. This eruption, estimated to have occurred around 74,000 years ago, unleashed an unimaginable amount of volcanic material, spewing ash and pumice into the atmosphere. The eruption was so massive that it triggered a volcanic winter, shrouding the planet in darkness and significantly impacting global climate.
The eruption’s epicenter was a supervolcano, a volcano capable of producing eruptions of unimaginable scale. Supervolcanoes are not characterized by a single, cone-shaped peak like traditional volcanoes, but rather by a massive magma chamber beneath the Earth’s surface. The immense pressure from the magma chamber eventually led to a catastrophic eruption, creating a massive caldera.
The Formation of the Caldera
The caldera, a large, bowl-shaped depression, is the defining feature of Lake Toba. It was formed when the supervolcano’s eruption emptied the magma chamber, causing the overlying rock to collapse inward. This collapse created a vast crater, which was later filled with water to form the lake we see today. The caldera’s rim is marked by a series of towering cliffs that rise up to 1,200 meters above the lake’s surface, a dramatic testament to the eruption’s power.
Geological Processes that Shaped the Landscape
The eruption’s impact extended far beyond the caldera. The volcanic ash and pumice deposited by the eruption covered a vast area, contributing to the formation of fertile soils in the surrounding region. The eruption also triggered a series of geological processes that shaped the landscape, including:
- Erosion: Over thousands of years, erosion by wind and water has carved out valleys, canyons, and other dramatic features in the landscape surrounding Lake Toba.
- Sedimentation: The volcanic ash and pumice deposited by the eruption have settled over time, forming layers of sediment that have enriched the soil and provided a substrate for the growth of vegetation.
- Faulting: The immense pressure from the eruption caused fractures and faults in the Earth’s crust, leading to the formation of new geological features and contributing to the landscape’s dramatic topography.
Comparing Lake Toba’s Caldera to Other Volcanic Calderas
Lake Toba’s caldera is one of the largest and most well-preserved volcanic calderas in the world. Here is a comparison of Lake Toba’s caldera with other notable volcanic calderas:
| Caldera | Location | Diameter (km) | Age (years) | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Toba | Sumatra, Indonesia | 100 | 74,000 | Largest volcanic lake in the world, formed by a supervolcanic eruption |
| Yellowstone Caldera | Wyoming, USA | 80 | 630,000 | Active supervolcano, known for its geysers and hot springs |
| Valles Caldera | New Mexico, USA | 22 | 1.2 million | Home to a volcanic field with numerous volcanic vents and lava flows |
| Aira Caldera | Kyushu, Japan | 20 | 22,000 | Active caldera, known for its volcanic activity and hot springs |
The Tourism Potential of Lake Toba

Lake Toba, nestled in the heart of North Sumatra, Indonesia, is a natural wonder that captivates visitors with its breathtaking beauty. The largest volcanic lake in the world, Lake Toba is home to a rich cultural heritage, diverse ecosystems, and stunning landscapes. This unique combination of natural beauty and cultural significance has made Lake Toba a prime destination for tourism, attracting both domestic and international visitors. This section delves into the tourism potential of Lake Toba, exploring its attractions, economic importance, challenges, and opportunities for sustainable tourism development.
Tourism Attractions and Activities, Asal usul danau toba bahasa inggris
Lake Toba offers a plethora of attractions and activities for tourists, catering to diverse interests and preferences. The lake itself, with its crystal-clear waters, is a magnet for water sports enthusiasts. Visitors can enjoy swimming, boating, fishing, and kayaking, immersing themselves in the serene beauty of the lake.
- Samosir Island: This volcanic island, located in the middle of Lake Toba, is a major tourist attraction. Visitors can explore the island’s traditional villages, learn about the Batak culture, and enjoy stunning views of the lake. Samosir Island is known for its unique Batak houses, built with traditional materials and adorned with intricate carvings.
- Sipiso-piso Waterfall: A magnificent waterfall cascading down a cliff, offering breathtaking views and opportunities for hiking and photography.
- Hot Springs: Several hot springs are located around Lake Toba, offering a relaxing and rejuvenating experience. Visitors can soak in the mineral-rich waters and enjoy the therapeutic benefits.
- Cultural Performances: Traditional Batak dance and music performances are a highlight of Lake Toba tourism. Visitors can witness the vibrant and energetic performances, gaining insights into the rich cultural heritage of the region.
Economic Importance of Tourism
Tourism plays a crucial role in the economic development of the Lake Toba region. It generates significant revenue, creates employment opportunities, and stimulates local businesses. The influx of tourists supports various sectors, including hospitality, transportation, food and beverage, and souvenir shops.
- Employment: Tourism creates jobs in various sectors, providing employment opportunities for local communities. This includes hotel staff, tour guides, transportation providers, and restaurant workers.
- Revenue Generation: Tourism generates significant revenue for the region through hotel bookings, entrance fees, souvenirs, and other tourist-related spending. This revenue contributes to the economic well-being of the local communities.
- Infrastructure Development: The growth of tourism in Lake Toba has led to infrastructure development, including improved roads, transportation facilities, and accommodation options. This development benefits not only tourists but also the local population.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Tourism Development
While Lake Toba holds immense tourism potential, there are challenges that need to be addressed to ensure sustainable tourism development.
- Environmental Protection: The natural beauty of Lake Toba is its greatest asset. Protecting the environment from pollution, deforestation, and unsustainable practices is crucial for the long-term sustainability of tourism.
- Infrastructure Development: While infrastructure development is necessary to accommodate tourist influx, it must be done sustainably, minimizing environmental impact and preserving the natural beauty of the region.
- Community Involvement: Local communities should be actively involved in tourism planning and development. This ensures that tourism benefits the local population and fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Cultural Preservation: Tourism can have both positive and negative impacts on local culture. It’s important to promote responsible tourism practices that respect and preserve the cultural heritage of the region.
Recommendations for Responsible Tourism Practices
- Minimize Environmental Impact: Tourists should be encouraged to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and using sustainable transportation options.
- Support Local Businesses: Tourists should prioritize spending their money at local businesses, contributing to the economic well-being of the communities.
- Respect Local Culture: Tourists should be mindful of local customs and traditions, dressing appropriately and respecting religious sensitivities.
- Engage with Local Communities: Tourists should interact with local communities, learn about their culture, and support local initiatives.
- Promote Sustainable Tourism: Tourists should advocate for sustainable tourism practices and support businesses that prioritize environmental protection and community involvement.
The Geography of Lake Toba: Asal Usul Danau Toba Bahasa Inggris
Lake Toba is a truly remarkable natural wonder, not just for its stunning beauty but also for its unique geological history. This caldera lake, nestled within the heart of Sumatra, is a testament to the immense power of nature. Its formation, a result of a massive volcanic eruption, has shaped the surrounding landscape and left a lasting impact on the region’s geography and ecology.
Physical Characteristics
Lake Toba is a vast body of water, stretching approximately 100 kilometers in length and 30 kilometers in width. Its surface area covers roughly 1,145 square kilometers, making it one of the largest volcanic lakes in the world. The lake’s depth is equally impressive, reaching a maximum of 505 meters, with an average depth of 450 meters. The surrounding terrain is characterized by rolling hills and mountains, creating a picturesque backdrop for the lake.
Location and Geographical Context
Lake Toba is situated in the northern part of Sumatra, Indonesia, specifically in the provinces of North Sumatra and Sumatra Utara. It lies within the Batak highlands, a region known for its unique culture and traditional villages. The lake’s location within the Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity, further highlights its significance in the context of global tectonics.
Role in the Water Cycle
Lake Toba plays a crucial role in the regional water cycle. It acts as a massive reservoir, regulating the flow of water in the surrounding area. The lake receives water from numerous rivers and streams that flow into it, and in turn, it provides water for irrigation, drinking, and other human activities. Its large surface area contributes to the regional climate by influencing rainfall patterns and moderating temperatures.
Importance as a Water Source
The lake’s vast water reserves make it a vital source of water for the surrounding communities. It supports a thriving fishing industry, providing livelihoods for many local residents. The lake’s water is also used for irrigation, contributing to the agricultural economy of the region. Additionally, Lake Toba’s waters are a valuable resource for hydropower generation, playing a role in meeting the energy needs of the area.
Map of Lake Toba and Surrounding Areas
A map of Lake Toba would showcase its location within the Batak highlands of Sumatra, Indonesia. It would also highlight the surrounding terrain, including the rolling hills and mountains that encircle the lake. The map could further indicate the major rivers and streams that flow into the lake, as well as the nearby towns and villages. This visual representation would provide a comprehensive understanding of the lake’s geographical context and its relationship to the surrounding landscape.
Kesimpulan Akhir

Danau Toba merupakan bukti kekuatan alam yang dahsyat dan keindahan alam yang mempesona. Kisah pembentukannya, budaya yang berkembang di sekitarnya, dan potensi wisata yang dimilikinya menjadikan Danau Toba sebagai destinasi yang kaya akan nilai sejarah, budaya, dan keindahan alam. Menjelajahi Danau Toba adalah perjalanan yang tak hanya mengagumi keindahan alam, tetapi juga menyelami kekayaan budaya dan sejarah yang terukir di dalamnya.