Mempelajari contoh laporan keuangan dalam bahasa Inggris sangat penting bagi siapa pun yang ingin memahami dunia bisnis global. Laporan keuangan merupakan bahasa universal yang digunakan untuk menyampaikan informasi finansial perusahaan kepada berbagai pihak, seperti investor, kreditur, dan regulator. Melalui contoh-contoh yang mudah dipahami, Anda dapat memahami struktur, terminologi, dan cara interpretasi laporan keuangan yang sering digunakan di dunia internasional.
Artikel ini akan membahas secara rinci berbagai aspek penting dari laporan keuangan, mulai dari definisi, elemen, struktur, format, hingga penerapannya dalam praktik. Dengan memahami contoh-contoh yang diberikan, Anda akan memiliki dasar yang kuat untuk menganalisis laporan keuangan perusahaan dan membuat keputusan bisnis yang tepat.
Financial Statements
Financial statements are a collection of reports that summarize a company’s financial performance and position. They are a crucial tool for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to understand a company’s financial health and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Financial Statements
The primary objective of financial statements is to provide a clear and concise picture of a company’s financial performance and position. They are designed to help stakeholders understand:
- The company’s profitability
- The company’s ability to generate cash flow
- The company’s financial structure
- The company’s assets and liabilities
Types of Financial Statements
| Statement | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Income Statement | IS | Summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period, typically a year or a quarter. |
| Balance Sheet | BS | Shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. |
| Statement of Cash Flows | SCF | Reports the movement of cash into and out of a company over a specific period. |
| Statement of Changes in Equity | SCE | Details the changes in a company’s equity over a specific period. |
Financial Statement Elements
Financial statements are the primary means by which companies communicate their financial performance and position to stakeholders. They provide a structured and standardized framework for presenting financial information, enabling users to make informed decisions about the company’s operations, profitability, and financial health. These statements are typically prepared on a periodic basis, usually quarterly or annually, and are typically audited by independent accounting firms to ensure their accuracy and reliability.
The elements of financial statements are the fundamental building blocks that make up the complete picture of a company’s financial performance. These elements are standardized across different companies and industries, allowing for comparability and analysis. Understanding the elements of financial statements is crucial for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders who rely on this information to make informed decisions.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, presents a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It follows the fundamental accounting equation, which states that assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity.
- Assets represent the resources controlled by the company that are expected to provide future economic benefits. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
- Liabilities represent the obligations of the company to external parties. Examples include accounts payable, salaries payable, loans payable, and bonds payable.
- Equity represents the ownership interest in the company, which is the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities. It includes contributed capital, retained earnings, and other comprehensive income.
The balance sheet is presented in a tabular format, typically with assets listed on the left side and liabilities and equity listed on the right side. It is usually arranged in order of liquidity, with the most liquid assets listed first and the least liquid assets listed last.
Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, presents a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It summarizes the revenues earned and expenses incurred during that period, resulting in net income or net loss.
- Revenues represent the income generated from the company’s primary operations. Examples include sales revenue, service revenue, and interest revenue.
- Expenses represent the costs incurred in generating revenues. Examples include cost of goods sold (COGS), salaries and wages, rent expense, and depreciation expense.
The income statement is typically presented in a vertical format, with revenues listed first, followed by expenses, and finally, net income or net loss. It may also include a breakdown of revenues and expenses by category, providing a more detailed view of the company’s financial performance.
Statement of Cash Flows
The statement of cash flows provides a summary of the cash inflows and outflows that occurred during a specific period. It classifies cash flows into three main categories: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
- Operating activities relate to the company’s core business operations. Examples include cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, and cash paid for salaries and wages.
- Investing activities relate to the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets. Examples include cash paid for property, plant, and equipment, cash received from the sale of investments, and cash paid for acquisitions.
- Financing activities relate to the company’s financing activities. Examples include cash received from issuing debt or equity, cash paid for dividends, and cash paid for debt repayment.
The statement of cash flows is typically presented in a vertical format, with cash flows from operating activities listed first, followed by cash flows from investing activities, and finally, cash flows from financing activities. It may also include a reconciliation of net income to cash flow from operating activities, providing a more detailed view of the company’s cash flow performance.
Statement of Changes in Equity
The statement of changes in equity reconciles the beginning and ending balances of equity for a specific period. It shows the changes in equity that occurred during that period, such as contributions from owners, net income, and dividends paid.
This statement is presented in a tabular format, with the beginning balance of equity listed first, followed by the changes in equity during the period, and finally, the ending balance of equity. It provides a comprehensive view of the changes in ownership interest in the company over time.
Notes to the Financial Statements
The notes to the financial statements provide additional information that is not presented in the main financial statements. These notes are crucial for understanding the company’s financial position and performance, as they provide context and explanations for the figures presented in the main statements.
The notes to the financial statements typically cover a wide range of topics, including accounting policies, significant assumptions, and details about specific items presented in the financial statements. They also disclose information about related-party transactions, contingent liabilities, and other important disclosures.
Contoh Laporan Keuangan Sederhana

Laporan keuangan adalah kumpulan data yang menunjukkan kondisi keuangan perusahaan pada periode tertentu. Laporan keuangan terdiri dari beberapa komponen utama, yaitu laporan laba rugi, neraca, dan laporan arus kas. Ketiga laporan ini saling berhubungan dan memberikan gambaran yang lengkap tentang kondisi keuangan perusahaan.
Contoh Laporan Keuangan Sederhana
Sebagai contoh, mari kita lihat laporan keuangan sederhana untuk perusahaan fiktif bernama “ABC Company” untuk tahun 2023.
Laporan Laba Rugi
Laporan laba rugi menunjukkan kinerja keuangan perusahaan selama periode tertentu, biasanya satu tahun. Berikut contoh laporan laba rugi untuk ABC Company:
| Item | Jumlah (Rp) |
|---|---|
| Pendapatan | 100.000.000 |
| Beban Pokok Penjualan | (50.000.000) |
| Beban Operasional | (20.000.000) |
| Laba Bruto | 30.000.000 |
| Laba Operasional | 10.000.000 |
| Laba Setelah Pajak | 7.000.000 |
Penjelasan:
- Pendapatan: Jumlah total pendapatan yang diterima perusahaan selama periode tersebut.
- Beban Pokok Penjualan: Biaya yang dikeluarkan untuk menghasilkan produk atau jasa yang dijual.
- Beban Operasional: Biaya yang dikeluarkan untuk menjalankan operasional perusahaan, seperti gaji, sewa, dan utilitas.
- Laba Bruto: Selisih antara pendapatan dan beban pokok penjualan.
- Laba Operasional: Selisih antara laba bruto dan beban operasional.
- Laba Setelah Pajak: Laba operasional setelah dikurangi pajak.
Neraca
Neraca menunjukkan kondisi keuangan perusahaan pada suatu titik waktu tertentu. Berikut contoh neraca untuk ABC Company pada tanggal 31 Desember 2023:
| Aset | Jumlah (Rp) |
|---|---|
| Aset Lancar | 50.000.000 |
| Aset Tetap | 100.000.000 |
| Total Aset | 150.000.000 |
| Liabilitas dan Ekuitas | Jumlah (Rp) |
| Liabilitas Lancar | 20.000.000 |
| Liabilitas Jangka Panjang | 30.000.000 |
| Ekuitas | 100.000.000 |
| Total Liabilitas dan Ekuitas | 150.000.000 |
Penjelasan:
- Aset: Apa yang dimiliki perusahaan, seperti kas, piutang, dan peralatan.
- Liabilitas: Apa yang dihutangi perusahaan, seperti utang kepada pemasok dan bank.
- Ekuitas: Selisih antara aset dan liabilitas, yang menunjukkan nilai bersih perusahaan.
Laporan Arus Kas
Laporan arus kas menunjukkan pergerakan kas perusahaan selama periode tertentu. Berikut contoh laporan arus kas untuk ABC Company untuk tahun 2023:
| Aktivitas Operasional | Jumlah (Rp) |
|---|---|
| Laba Setelah Pajak | 7.000.000 |
| Penyesuaian Non-Kas | (2.000.000) |
| Arus Kas dari Operasional | 5.000.000 |
| Aktivitas Investasi | Jumlah (Rp) |
| Pembelian Aset Tetap | (10.000.000) |
| Arus Kas dari Investasi | (10.000.000) |
| Aktivitas Pendanaan | Jumlah (Rp) |
| Penerimaan Pinjaman | 15.000.000 |
| Pembayaran Dividen | (3.000.000) |
| Arus Kas dari Pendanaan | 12.000.000 |
| Total Arus Kas | 7.000.000 |
Penjelasan:
- Aktivitas Operasional: Pergerakan kas yang berasal dari kegiatan operasional perusahaan, seperti penjualan dan pembelian barang.
- Aktivitas Investasi: Pergerakan kas yang berasal dari kegiatan investasi, seperti pembelian aset tetap.
- Aktivitas Pendanaan: Pergerakan kas yang berasal dari kegiatan pendanaan, seperti penerimaan pinjaman dan pembayaran dividen.
Financial Statement Structure
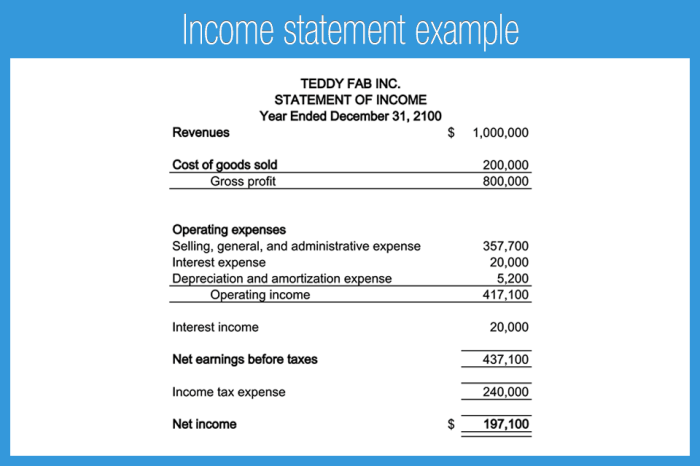
Financial statements are the official reports that summarize the financial performance and position of a company. They are crucial for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions about the company. To ensure clarity and consistency, financial statements follow a standardized structure. This structure ensures that all essential information is presented in a consistent and understandable format, regardless of the company’s size or industry.
Components of Financial Statements
Financial statements typically consist of four main components:
- Balance Sheet: This statement presents a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It shows what the company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the value of the owners’ stake in the company (equity). The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
- Income Statement: Also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, this report summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and net income or loss over a specific period. It shows how much revenue the company generated, the costs associated with generating that revenue, and the resulting profit or loss.
- Statement of Cash Flows: This statement tracks the movement of cash into and out of a company during a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into three main activities: operating, investing, and financing. The statement of cash flows provides insights into the company’s ability to generate cash, its investments, and its financing activities.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: This statement explains the changes in a company’s equity over a specific period. It shows how much equity has increased or decreased due to factors such as profits, losses, dividends, and share issuance or repurchases.
Example of Financial Statement Structure
Imagine a company called “Tech Solutions” that provides software development services. Its financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023, would be structured as follows:
| Financial Statement | Content |
|---|---|
| Balance Sheet | Assets: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E), etc. Liabilities: Accounts Payable, Notes Payable, Deferred Revenue, etc. Equity: Common Stock, Retained Earnings, etc. |
| Income Statement | Revenue: Software Development Services Revenue Expenses: Cost of Goods Sold, Salaries and Wages, Rent, Utilities, Depreciation, etc. Net Income (or Loss) |
| Statement of Cash Flows | Operating Activities: Cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, etc. Investing Activities: Purchase of equipment, sale of investments, etc. Financing Activities: Issuance of stock, payment of dividends, etc. |
| Statement of Changes in Equity | Beginning Equity Add: Net Income Less: Dividends Paid Ending Equity |
Information Flow Between Financial Statements
The four main financial statements are interconnected and provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. Here’s how information flows between them:
- Net Income from the Income Statement flows into the Statement of Changes in Equity. This reflects the impact of profits or losses on the company’s equity.
- Changes in equity from the Statement of Changes in Equity are reflected in the Balance Sheet. This ensures that the balance sheet reflects the updated value of equity.
- Cash flows from the Statement of Cash Flows are used to adjust the cash balance on the Balance Sheet. This ensures that the balance sheet accurately reflects the company’s cash position.
Financial Statement Terminology: Contoh Laporan Keuangan Dalam Bahasa Inggris
Financial statements are a key part of understanding a company’s financial health. They provide a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. To understand these statements, it is important to be familiar with the terminology used.
Common Financial Statement Terminology
Here is a list of common financial statement terminology and their definitions:
| Terminology | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | Resources controlled by the company as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the company. | Cash, accounts receivable, inventory, equipment |
| Liabilities | Present obligations of the company arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from resources embodying economic benefits. | Accounts payable, salaries payable, notes payable |
| Equity | The residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting all its liabilities. | Common stock, retained earnings |
| Revenue | Increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from equity participants. | Sales revenue, service revenue, interest revenue |
| Expenses | Decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletions of assets or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants. | Cost of goods sold, salaries expense, rent expense |
| Net Income | The difference between revenues and expenses for a period. | If a company has $100,000 in revenue and $50,000 in expenses, its net income is $50,000. |
| Balance Sheet | A financial statement that reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. | The balance sheet shows a company’s financial position at a particular moment. |
| Income Statement | A financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses for a period of time. | The income statement shows a company’s profitability over a period of time. |
| Statement of Cash Flows | A financial statement that reports a company’s cash inflows and outflows for a period of time. | The statement of cash flows shows how much cash a company has generated and used during a period of time. |
| Statement of Changes in Equity | A financial statement that reports the changes in a company’s equity for a period of time. | The statement of changes in equity shows how a company’s equity has changed during a period of time. |
Interpretasi Laporan Keuangan
Financial statements are the language of business. They provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health and performance. Understanding how to interpret these statements is crucial for making informed decisions about investments, credit, and other financial matters.
Analisis Laporan Keuangan
Financial statement analysis is the process of examining a company’s financial statements to gain insights into its financial health and performance. This involves comparing financial data over time, evaluating key ratios, and identifying trends.
Contoh Penggunaan Laporan Keuangan
Laporan keuangan dapat digunakan untuk menganalisis kinerja perusahaan dengan berbagai cara. Misalnya, seorang investor dapat menggunakan laporan keuangan untuk menilai apakah sebuah perusahaan layak untuk diinvestasikan. Seorang kreditur dapat menggunakan laporan keuangan untuk menilai kemampuan perusahaan untuk melunasi hutang.
Pertanyaan untuk Menganalisis Laporan Keuangan
Ada sejumlah pertanyaan yang dapat digunakan untuk menganalisis laporan keuangan. Berikut adalah beberapa contohnya:
- Bagaimana kinerja perusahaan dalam hal profitabilitas?
- Bagaimana kinerja perusahaan dalam hal likuiditas?
- Bagaimana kinerja perusahaan dalam hal solvabilitas?
- Bagaimana kinerja perusahaan dalam hal efisiensi?
- Bagaimana kinerja perusahaan dalam hal pertumbuhan?
Analisis Rasio Keuangan
Financial ratios are a key tool for interpreting financial statements. These ratios provide a standardized way to compare a company’s financial performance to its peers, industry averages, or its own historical performance.
Contoh Rasio Keuangan
Berikut adalah beberapa contoh rasio keuangan yang umum digunakan:
- Rasio Profitabilitas: Mengukur kemampuan perusahaan untuk menghasilkan keuntungan. Contohnya, rasio laba bersih terhadap penjualan, rasio laba bersih terhadap aset, dan rasio laba bersih terhadap ekuitas.
- Rasio Likuiditas: Mengukur kemampuan perusahaan untuk memenuhi kewajiban jangka pendeknya. Contohnya, rasio lancar, rasio cepat, dan rasio kas.
- Rasio Solvabilitas: Mengukur kemampuan perusahaan untuk memenuhi kewajiban jangka panjangnya. Contohnya, rasio hutang terhadap ekuitas, rasio hutang terhadap aset, dan rasio likuiditas jangka panjang.
- Rasio Efisiensi: Mengukur efisiensi perusahaan dalam menggunakan asetnya. Contohnya, perputaran persediaan, perputaran piutang, dan perputaran aset.
- Rasio Pertumbuhan: Mengukur tingkat pertumbuhan perusahaan. Contohnya, tingkat pertumbuhan penjualan, tingkat pertumbuhan laba bersih, dan tingkat pertumbuhan ekuitas.
Analisis Tren
Financial statement analysis also involves identifying trends in a company’s financial performance. This can be done by comparing financial data over time, such as year-over-year or quarter-over-quarter comparisons.
Contoh Analisis Tren
Misalnya, jika perusahaan mengalami penurunan dalam rasio laba bersih terhadap penjualan selama beberapa tahun terakhir, ini bisa menjadi tanda bahwa perusahaan menghadapi tantangan dalam profitabilitas.
Kesimpulan
Interpretasi laporan keuangan adalah proses yang kompleks dan membutuhkan pemahaman yang mendalam tentang prinsip akuntansi dan analisis keuangan. Namun, dengan menggunakan alat dan teknik yang tepat, investor, kreditur, dan pihak terkait lainnya dapat memperoleh informasi yang berharga tentang kinerja keuangan perusahaan.
Accounting Standards
Accounting standards are a set of rules and guidelines that dictate how financial information is recorded, presented, and disclosed in financial statements. They are crucial for ensuring consistency, transparency, and comparability of financial information across different companies and industries. These standards provide a framework for preparing financial statements that are reliable and understandable to users, such as investors, creditors, and regulators.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP is the most widely used set of accounting standards in the United States. It is developed and maintained by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). GAAP aims to ensure that financial statements are accurate, reliable, and consistent. This standard provides guidance on various aspects of accounting, including revenue recognition, expense recognition, asset valuation, and liability recognition.
- GAAP emphasizes the importance of accrual accounting, which recognizes revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
- It also requires companies to disclose important information about their financial performance, including their accounting policies, significant assumptions, and any changes in accounting methods.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
IFRS is another widely used set of accounting standards. It is developed and maintained by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). IFRS aims to provide a common language for financial reporting globally. Many countries around the world have adopted IFRS, making it a globally recognized standard. IFRS is similar to GAAP in its principles but differs in certain areas.
- IFRS generally uses a principles-based approach, allowing for more flexibility in applying accounting rules to specific situations.
- GAAP, on the other hand, is more rules-based, providing specific guidance for a wide range of accounting transactions.
Comparison of GAAP and IFRS
| Feature | GAAP | IFRS |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Primarily used in the United States | Used in over 140 countries worldwide |
| Approach | Rules-based | Principles-based |
| Revenue Recognition | Specific guidance for different types of revenue | More general principles, allowing for more flexibility |
| Inventory Valuation | Allows for different methods, such as FIFO and LIFO | Generally requires the use of the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method |
| Leases | Uses a specific accounting model for leases | Uses a single model for all leases |
Impact of Accounting Standards on Financial Statements
Accounting standards have a significant impact on the preparation of financial statements. They determine how financial transactions are recorded, measured, and presented. For example, GAAP requires companies to use accrual accounting, which means that revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. This can have a significant impact on a company’s reported net income. For example, if a company sells goods on credit, it will recognize revenue when the goods are delivered, even if it hasn’t received cash payment yet. This can lead to a higher reported net income than if the company used a cash-basis accounting method.
Another example is the impact of accounting standards on the valuation of assets. GAAP requires companies to value their assets at their historical cost, which is the amount paid for the asset when it was acquired. However, IFRS allows for the use of fair value accounting, which values assets at their current market value. This can have a significant impact on a company’s reported assets and equity. For example, if a company owns a piece of land that has increased in value since it was purchased, IFRS would allow the company to recognize the increase in value on its financial statements, while GAAP would not.
Accounting Principles
Accounting principles are a set of guidelines that govern how financial information is recorded, classified, and presented in financial statements. These principles ensure that financial information is consistent, reliable, and comparable across different companies and time periods. By adhering to these principles, businesses can provide a clear and accurate picture of their financial performance and position.
General Accounting Principles
There are several general accounting principles that are fundamental to the preparation of financial statements. These principles are:
- Going Concern: This principle assumes that a business will continue to operate in the foreseeable future. This assumption is important for valuing assets and liabilities, as well as for making decisions about future investments.
- Accrual Accounting: This principle requires that revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. For example, if a company sells goods on credit, the revenue is recognized when the goods are delivered, not when the cash is received.
- Matching Principle: This principle states that expenses should be matched with the revenues they generate. For example, the cost of goods sold should be matched with the revenue generated from the sale of those goods.
- Materiality: This principle states that only information that is material to the financial statements should be disclosed. Materiality is a matter of professional judgment, but it generally refers to information that could influence the decisions of users of the financial statements.
- Consistency: This principle requires that accounting methods are applied consistently from one period to the next. This ensures that financial statements are comparable over time.
- Full Disclosure: This principle requires that all relevant information that could affect the decisions of users of the financial statements should be disclosed. This includes information about significant events, accounting policies, and other relevant matters.
Examples of Accounting Principles in Action
Here are some examples of how accounting principles are applied in the preparation of financial statements:
- Going Concern: When a company is preparing its financial statements, it assumes that it will continue to operate in the foreseeable future. This assumption is important for valuing assets and liabilities, as well as for making decisions about future investments. For example, a company might purchase a piece of equipment with a useful life of 10 years. If the company assumes that it will continue to operate for at least 10 years, it will depreciate the equipment over its useful life. However, if the company is facing financial difficulties, it might not be able to continue to operate for 10 years. In this case, the company might need to depreciate the equipment over a shorter period.
- Accrual Accounting: When a company sells goods on credit, it recognizes the revenue when the goods are delivered, not when the cash is received. For example, if a company sells $100,000 worth of goods on credit on January 1st, it will recognize the $100,000 in revenue on January 1st, even if it doesn’t receive the cash until February 1st. This is because the company has earned the revenue when it delivered the goods.
- Matching Principle: When a company incurs an expense, it should match that expense with the revenue it generates. For example, if a company incurs $10,000 in advertising expenses to generate $20,000 in sales, it will match the $10,000 in expenses with the $20,000 in revenue. This ensures that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect the relationship between its expenses and revenues.
- Materiality: A company might not disclose information about a small expense, such as the cost of a new stapler. However, it would disclose information about a large expense, such as the cost of a new building. This is because the cost of a new stapler is not material to the financial statements, while the cost of a new building is.
- Consistency: A company should use the same accounting methods from one period to the next. For example, if a company uses the straight-line method to depreciate its equipment, it should continue to use the straight-line method in future periods. This ensures that the company’s financial statements are comparable over time.
- Full Disclosure: A company might disclose information about a significant event, such as a lawsuit or a change in accounting policy. This information is important because it could affect the decisions of users of the financial statements.
Table of Accounting Principles
| Principle | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Going Concern | Assumes that a business will continue to operate in the foreseeable future. | A company purchases a piece of equipment with a useful life of 10 years. The company depreciates the equipment over its useful life because it assumes it will continue to operate for at least 10 years. |
| Accrual Accounting | Requires that revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. | A company sells $100,000 worth of goods on credit on January 1st. The company recognizes the $100,000 in revenue on January 1st, even if it doesn’t receive the cash until February 1st. |
| Matching Principle | States that expenses should be matched with the revenues they generate. | A company incurs $10,000 in advertising expenses to generate $20,000 in sales. The company matches the $10,000 in expenses with the $20,000 in revenue. |
| Materiality | States that only information that is material to the financial statements should be disclosed. | A company might not disclose information about a small expense, such as the cost of a new stapler. However, it would disclose information about a large expense, such as the cost of a new building. |
| Consistency | Requires that accounting methods are applied consistently from one period to the next. | A company uses the straight-line method to depreciate its equipment. It continues to use the straight-line method in future periods. |
| Full Disclosure | Requires that all relevant information that could affect the decisions of users of the financial statements should be disclosed. | A company discloses information about a significant event, such as a lawsuit or a change in accounting policy. |
Penerapan dalam Praktik
Laporan keuangan adalah alat penting bagi berbagai pihak dalam dunia bisnis. Mereka tidak hanya memberikan gambaran tentang kinerja keuangan suatu perusahaan, tetapi juga membantu dalam pengambilan keputusan yang strategis.
Contoh Kasus Nyata
Bayangkan sebuah perusahaan teknologi rintisan yang sedang mencari pendanaan dari investor. Investor potensial akan melihat laporan keuangan perusahaan tersebut untuk menilai potensi pertumbuhan, profitabilitas, dan kesehatan keuangannya. Mereka akan menganalisis rasio keuangan, arus kas, dan catatan keuangan lainnya untuk menentukan apakah investasi mereka akan memberikan pengembalian yang baik. Laporan keuangan menjadi alat penting dalam menarik investor dan mendapatkan pendanaan yang dibutuhkan untuk mengembangkan bisnis.
Peran Laporan Keuangan dalam Pengambilan Keputusan Bisnis
Laporan keuangan tidak hanya penting bagi investor, tetapi juga bagi manajemen perusahaan. Mereka menggunakannya untuk:
- Memantau kinerja perusahaan: Laporan keuangan membantu manajemen dalam melihat kinerja perusahaan secara keseluruhan, seperti profitabilitas, efisiensi, dan likuiditas. Mereka dapat mengidentifikasi area yang perlu ditingkatkan dan mengambil langkah-langkah yang diperlukan untuk mencapai tujuan bisnis.
- Merencanakan strategi bisnis: Laporan keuangan memberikan informasi penting untuk merumuskan strategi bisnis yang efektif. Manajemen dapat menggunakan data keuangan untuk memprediksi tren pasar, mengidentifikasi peluang investasi, dan menetapkan target keuangan yang realistis.
- Mengambil keputusan operasional: Laporan keuangan membantu manajemen dalam membuat keputusan operasional, seperti pengadaan bahan baku, manajemen inventaris, dan pengalokasian sumber daya.
Dialog Investor dan Manajemen Perusahaan, Contoh laporan keuangan dalam bahasa inggris
Berikut ini adalah contoh dialog antara seorang investor (I) dan manajer keuangan (M) perusahaan yang membahas laporan keuangan:
I: “Saya tertarik untuk berinvestasi di perusahaan Anda. Bisakah Anda jelaskan tentang kinerja keuangan perusahaan dalam beberapa tahun terakhir?”
M: “Tentu. Dalam laporan keuangan kami, Anda dapat melihat bahwa pendapatan perusahaan telah meningkat secara konsisten selama tiga tahun terakhir. Kami juga telah berhasil meningkatkan profitabilitas dan mengelola arus kas secara efektif.”
I: “Saya melihat bahwa rasio hutang terhadap ekuitas Anda cukup tinggi. Bagaimana Anda mengelola risiko keuangan tersebut?”
M: “Kami menyadari bahwa rasio hutang terhadap ekuitas kami cukup tinggi. Namun, kami memiliki strategi yang jelas untuk mengurangi rasio tersebut dalam beberapa tahun ke depan. Kami juga memiliki cadangan kas yang cukup untuk memenuhi kewajiban keuangan kami.”
I: “Terima kasih atas penjelasannya. Saya akan mempelajari laporan keuangan Anda lebih lanjut sebelum membuat keputusan investasi.”
Penutup
Dengan memahami contoh laporan keuangan dalam bahasa Inggris, Anda akan memiliki alat yang berharga untuk memahami kinerja perusahaan, menilai risiko investasi, dan membuat keputusan bisnis yang lebih terinformasi. Mempelajari contoh-contoh ini juga akan membantu Anda meningkatkan kemampuan berbahasa Inggris dalam konteks bisnis dan keuangan, yang sangat bermanfaat dalam era globalisasi saat ini.