Nama nama akun dalam akuntansi bahasa inggris – Akuntansi, sebuah bahasa universal dalam dunia bisnis, memiliki terminologi yang perlu dipahami untuk mengelola keuangan dengan baik. Dalam bahasa Inggris, memahami nama akun menjadi kunci untuk menafsirkan laporan keuangan dan membuat keputusan bisnis yang tepat. Dari aset hingga kewajiban, setiap akun memiliki peranan penting dalam menggambarkan kondisi keuangan suatu perusahaan.
Artikel ini akan menjelajahi berbagai jenis akun dalam akuntansi bahasa Inggris, mulai dari aset dan kewajiban hingga pendapatan dan beban. Dengan memahami istilah-istilah ini, Anda akan memiliki pemahaman yang lebih baik tentang cara kerja akuntansi dan bagaimana informasi tersebut dapat digunakan untuk membuat keputusan bisnis yang lebih cerdas.
Liability Accounts
Liability accounts are essential components of the accounting equation, representing financial obligations or debts owed by a business to external parties. They reflect the company’s financial commitments and obligations to creditors, suppliers, and other stakeholders. These accounts are categorized based on the timeframe for settling the debt, namely short-term and long-term liabilities.
Short-Term and Long-Term Liabilities
The primary distinction between short-term and long-term liabilities lies in their maturity period. Short-term liabilities, also known as current liabilities, are obligations that are expected to be settled within a year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer. Conversely, long-term liabilities, also known as non-current liabilities, are obligations that extend beyond a year or the operating cycle.
Common Examples of Liability Accounts
- Accounts Payable: This account represents the amount owed to suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit. It is a common short-term liability.
- Notes Payable: Notes payable are written promises to pay a specific amount of money on a specific date. They can be short-term or long-term, depending on the maturity period.
- Salaries Payable: This account reflects the amount owed to employees for their salaries or wages that have been earned but not yet paid.
- Interest Payable: This account represents the accrued interest owed on borrowed funds or other financial obligations.
- Taxes Payable: This account reflects the amount of taxes owed to the government, such as income tax, sales tax, or property tax.
- Deferred Revenue: This account represents the revenue received for goods or services that have not yet been delivered or performed. It is considered a liability because the business has an obligation to provide the goods or services in the future.
- Long-Term Debt: This category encompasses various long-term liabilities, such as bonds payable, mortgages payable, and loans payable. These obligations typically have a maturity period exceeding one year.
Revenue Account Names
Revenue accounts are the lifeblood of any business, as they represent the money earned from the core operations of the company. In accounting, revenue accounts are used to record the income generated from selling goods or services. This article delves into the various revenue account names commonly used in English accounting, along with their Indonesian translations, providing a comprehensive understanding of how they are categorized and utilized in financial reporting.
Types of Revenue Accounts
Revenue accounts are classified based on the nature of the income generated. The most common types of revenue accounts include:
- Sales Revenue: This is the primary revenue account for most businesses. It represents the income generated from selling goods or services to customers. In Indonesian, it is translated as “Pendapatan Penjualan.” For example, a retail store would record sales of clothing, electronics, or other merchandise under this account.
- Service Revenue: This account is used to record income generated from providing services to customers. In Indonesian, it is translated as “Pendapatan Jasa.” For example, a consulting firm would record fees earned for providing business advice or a hair salon would record income from haircuts and styling services.
- Interest Revenue: This account is used to record income earned from interest on investments or loans. In Indonesian, it is translated as “Pendapatan Bunga.” For example, a bank would record interest earned on deposits held by customers.
- Rent Revenue: This account is used to record income earned from renting out property. In Indonesian, it is translated as “Pendapatan Sewa.” For example, a landlord would record rent payments received from tenants.
- Dividend Revenue: This account is used to record income earned from dividends received from investments in stocks or other equity securities. In Indonesian, it is translated as “Pendapatan Dividen.” For example, an investor would record dividends received from shares held in a company.
Using Revenue Accounts in the Income Statement
Revenue accounts play a crucial role in the income statement, which is a financial statement that summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. The income statement is also known as the profit and loss statement (P&L). The revenue accounts are listed at the top of the income statement, and they are then deducted by expenses to arrive at the company’s net income or loss.
The formula for calculating net income is: Net Income = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
Examples of Common Revenue Accounts
Here are some examples of common revenue accounts used in accounting:
| English Account Name | Indonesian Account Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | Pendapatan Penjualan | Income generated from selling goods or services. |
| Service Revenue | Pendapatan Jasa | Income generated from providing services. |
| Interest Revenue | Pendapatan Bunga | Income earned from interest on investments or loans. |
| Rent Revenue | Pendapatan Sewa | Income earned from renting out property. |
| Dividend Revenue | Pendapatan Dividen | Income earned from dividends received from investments. |
Nama Akun Penghasilan: Nama Nama Akun Dalam Akuntansi Bahasa Inggris

Nama akun penghasilan merupakan salah satu elemen penting dalam akuntansi. Penghasilan merupakan sumber utama pendapatan bagi suatu perusahaan, dan pengelompokan akun penghasilan yang tepat dapat membantu dalam menganalisis kinerja keuangan perusahaan.
Tabel Nama Akun Penghasilan, Nama nama akun dalam akuntansi bahasa inggris
Berikut tabel yang berisi nama akun penghasilan dalam akuntansi bahasa Inggris dan terjemahannya dalam bahasa Indonesia:
| Nama Akun Penghasilan (Bahasa Inggris) | Nama Akun Penghasilan (Bahasa Indonesia) |
|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | Pendapatan Penjualan |
| Service Revenue | Pendapatan Jasa |
| Interest Revenue | Pendapatan Bunga |
| Rent Revenue | Pendapatan Sewa |
| Dividend Revenue | Pendapatan Deviden |
| Gain on Sale of Assets | Keuntungan Penjualan Aset |
Perbedaan Antara Akun Pendapatan dan Akun Penghasilan
Akun pendapatan dan akun penghasilan seringkali digunakan secara bergantian, namun terdapat perbedaan penting antara keduanya. Akun pendapatan merujuk pada pendapatan utama yang dihasilkan dari aktivitas bisnis utama perusahaan, seperti penjualan barang atau jasa. Sementara akun penghasilan mencakup pendapatan yang diperoleh dari sumber lain selain aktivitas bisnis utama, seperti pendapatan bunga, pendapatan sewa, dan keuntungan penjualan aset.
Contoh Akun Penghasilan
Berikut beberapa contoh akun penghasilan yang umum digunakan dalam akuntansi:
- Pendapatan bunga dari deposito di bank
- Keuntungan penjualan aset tetap, seperti kendaraan atau tanah
- Pendapatan sewa dari properti yang disewakan
- Pendapatan deviden dari saham yang dimiliki
Expense Account Names
Expense accounts are essential components of financial statements, particularly the income statement. These accounts track the costs incurred by a business in its operations, helping to determine profitability and make informed financial decisions.
Understanding Expense Accounts
Expense accounts are used to record the cost of resources consumed or used up in the process of generating revenue. These costs can include items like salaries, rent, utilities, supplies, and advertising. They are typically presented on the income statement, where they are subtracted from revenue to arrive at net income or profit.
Types of Expense Accounts
There are numerous types of expense accounts, each representing a different category of cost. Some common examples include:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This account represents the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods sold by a business. For manufacturing companies, COGS includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. For retailers, COGS includes the cost of purchasing goods from suppliers.
- Selling Expenses: These expenses are incurred in the process of marketing and selling goods or services. They can include advertising, sales commissions, and salaries of sales staff.
- Administrative Expenses: These expenses are incurred in the general administration and management of the business. They can include salaries of administrative staff, rent, utilities, and office supplies.
- Depreciation and Amortization: These expenses reflect the decline in value of long-term assets over time. Depreciation is used for tangible assets like equipment, while amortization is used for intangible assets like patents and copyrights.
- Interest Expense: This expense represents the cost of borrowing money. It is recorded when a company pays interest on loans or other debt.
- Rent Expense: This expense is incurred for the use of leased property, including office space, retail stores, or manufacturing facilities.
- Salaries and Wages Expense: This expense represents the cost of employee compensation, including salaries, wages, bonuses, and payroll taxes.
How Expense Accounts Are Used
Expense accounts are used in the following ways:
- Tracking Costs: Expense accounts provide a detailed record of all costs incurred by a business. This information is essential for monitoring expenses, identifying areas for cost reduction, and making informed financial decisions.
- Calculating Profitability: By subtracting expenses from revenue, businesses can determine their profitability. This information is crucial for evaluating the performance of the business and making decisions about pricing, product development, and investment.
- Preparing Financial Statements: Expense accounts are a key component of the income statement, which is one of the primary financial statements used by businesses to report their financial performance.
Examples of Expense Accounts
Here are some specific examples of expense accounts commonly used in accounting:
| Expense Account Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Advertising Expense | Costs associated with promoting goods or services. |
| Insurance Expense | Premiums paid for insurance coverage. |
| Office Supplies Expense | Cost of office supplies, such as paper, pens, and folders. |
| Telephone Expense | Costs associated with telephone services. |
| Travel Expense | Costs associated with business travel, such as airfare, hotel accommodations, and meals. |
| Utilities Expense | Costs associated with utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water. |
Inventory Account Names
Inventory is a crucial asset for businesses that sell goods. It represents the raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods that a company has on hand to sell. Inventory accounts are used to track the cost of inventory and its changes over time. These accounts are essential for accurately calculating a company’s profit and determining its financial health.
Inventory Account Names in English and Indonesian
Here is a table of common inventory account names in English and their Indonesian translations:
| English | Indonesian |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Bahan Baku |
| Work-in-Progress | Barang Dalam Proses |
| Finished Goods | Barang Jadi |
| Inventory | Persediaan |
| Cost of Goods Sold | Harga Pokok Penjualan |
Types of Inventory Accounts
Inventory accounts are classified based on the stage of production of the goods. The three main types of inventory accounts are:
- Raw Materials: These are the basic materials used in the production process. Examples include wood, metal, fabric, and chemicals.
- Work-in-Progress: This represents goods that are partially completed but not yet ready for sale. For example, a car that is being assembled or a piece of furniture that is being painted.
- Finished Goods: These are goods that are ready to be sold to customers. Examples include cars, furniture, clothing, and food.
How Inventory Accounts are Used in Financial Statements
Inventory accounts are used in both the balance sheet and the income statement. On the balance sheet, inventory is listed as an asset. It represents the value of the company’s inventory on hand at a specific point in time. The value of inventory is typically determined using the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) method.
On the income statement, inventory is used to calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS). COGS is the direct cost of producing the goods that are sold during a period. It includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. The formula for calculating COGS is:
Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory = Cost of Goods Sold
Examples of Common Inventory Accounts
Here are some examples of common inventory accounts used in accounting:
- Raw Materials Inventory: This account tracks the cost of raw materials purchased by a company.
- Work-in-Process Inventory: This account tracks the cost of goods that are still in the production process.
- Finished Goods Inventory: This account tracks the cost of goods that are ready to be sold.
- Cost of Goods Sold: This account tracks the cost of goods that have been sold during a period.
Accounts Receivable
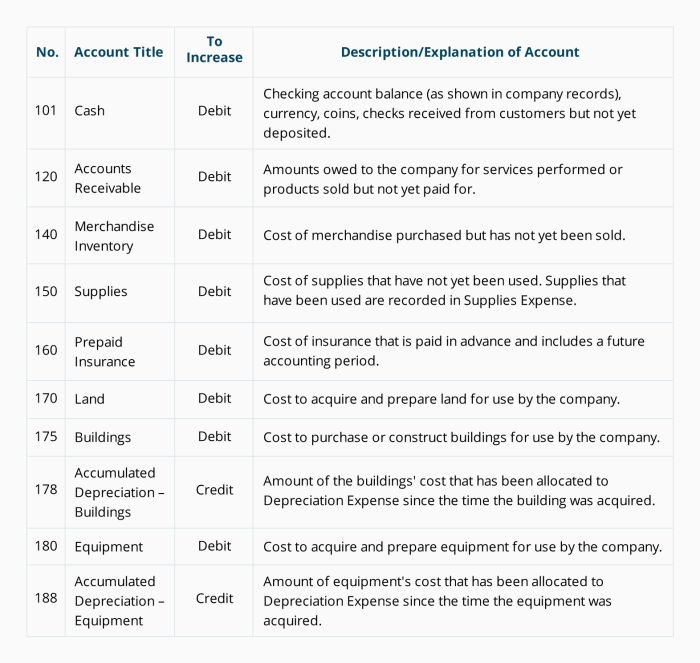
Accounts receivable, also known as debtors, is a balance of money due to you for goods or services that have already been delivered or used but not yet paid for by customers. It is an asset on a company’s balance sheet, representing the amount of money the company expects to receive from its customers.
How Accounts Receivable is Used in Financial Statements
Accounts receivable plays a crucial role in both the balance sheet and the income statement. In the balance sheet, accounts receivable is listed as a current asset, representing the company’s short-term assets that are expected to be converted into cash within a year. In the income statement, accounts receivable is used to calculate the net sales revenue.
Common Accounts Receivable Examples
Here are some common examples of accounts receivable:
- Sales on credit to customers
- Services provided to customers on credit
- Loans extended to customers
- Advances paid to suppliers for goods or services not yet received
The Importance of Managing Accounts Receivable
Managing accounts receivable effectively is crucial for a company’s financial health. By ensuring timely collection of payments, companies can improve cash flow and reduce the risk of bad debts.
Ringkasan Penutup
Memahami nama akun dalam akuntansi bahasa Inggris adalah langkah penting dalam menguasai dunia bisnis. Dengan pengetahuan ini, Anda dapat menafsirkan laporan keuangan, memahami kinerja perusahaan, dan membuat keputusan bisnis yang lebih tepat. Selalu ingat untuk terus belajar dan memperbarui pengetahuan Anda tentang terminologi akuntansi, karena hal ini akan membantu Anda dalam meraih kesuksesan di dunia bisnis.